2061 2017-09-20 2020-06-25
前言:在看完常用的ArrayList后,我们来看下LinkedList的实现。
一、类结构
1、概述
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
transient int size = 0;
// 头节点
transient Node<E> first;
// 尾节点
transient Node<E> last;
}
常规的类结构声明,与ArrayList相比,LinkedList在实现上有所不同。其中需要注意的
- AbstractSequentialList:是一个链式列表存储的规范,尽大程度的减少链式存储结构实现List接口所需的工作。
- Deque:double ended queue的缩写,Deque(英['dek] )是一个双端队列,父类是Queue(英[kju:])。这个需要重点看下。
2、内部类
既然是链式存储,那么链的节点是必不可少的,如下
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
二、Deque
1、定义
一个线性 collection,支持在两端插入和移除元素。名称 deque 是“double ended queue(双端队列)”的缩写,通常读为“deck”。大多数 Deque 实现对于它们能够包含的元素数没有固定限制,但此接口既支持有容量限制的双端队列,也支持没有固定大小限制的双端队列。
public interface Deque<E> extends Queue<E> {
// 失败时抛出异常,添加元素
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the front of this deque if it is
* possible to do so immediately without violating capacity restrictions,
* throwing an {@code IllegalStateException} if no space is currently
* available. When using a capacity-restricted deque, it is generally
* preferable to use method {@link #offerFirst}.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @throws IllegalStateException if the element cannot be added at this
* time due to capacity restrictions
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified element
* prevents it from being added to this deque
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and this
* deque does not permit null elements
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of the specified
* element prevents it from being added to this deque
*/
void addFirst(E e);
void addLast(E e);
// 失败时返回特殊值,添加元素,下同
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the front of this deque unless it would
* violate capacity restrictions. When using a capacity-restricted deque,
* this method is generally preferable to the {@link #addFirst} method,
* which can fail to insert an element only by throwing an exception.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @return {@code true} if the element was added to this deque, else
* {@code false}
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified element
* prevents it from being added to this deque
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and this
* deque does not permit null elements
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of the specified
* element prevents it from being added to this deque
*/
boolean offerFirst(E e);
boolean offerLast(E e);
E removeFirst();
E removeLast();
E pollFirst();
E pollLast();
E getFirst();
E getLast();
E peekFirst();
E peekLast();
// 移除第一次出现的元素,从first遍历
boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o);
// 移除最后一次出现的元素,从last遍历
boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o);
// *** Queue methods ***
// 失败时抛出异常,添加元素
boolean add(E e);
// 返回特殊值
boolean offer(E e);
// 失败时抛出异常,删除元素并返回
E remove();
E poll();
// 失败时抛出异常,返回首元素,不删除
E element();
E peek();
// *** Stack methods ***
//入栈
void push(E e);
// 出栈
E pop();
// *** Collection methods ***
boolean remove(Object o);
boolean contains(Object o);
public int size();
Iterator<E> iterator();
Iterator<E> descendingIterator();
}
// Queue接口与List、Set接口是平级
public interface Queue<E> extends Collection<E> {
//方法略
}
此接口定义在双端队列两端访问元素的方法。提供插入、移除和检查元素的方法。每种方法都存在两种形式:
- 一种形式在操作失败时抛出异常(如因容量限制插入失败,size为0去取值)。
- 另一种形式返回一个特殊值(null 或 false,具体取决于操作)。
插入操作的后一种形式是专为使用有容量限制的 Deque 实现设计的;在大多数实现中,插入操作不能失败。
2、可用作于队列
此接口扩展了 Queue 接口。在将双端队列用作队列时,将得到 FIFO(先进先出)行为。将元素添加到双端队列的末尾,从双端队列的开头移除元素。从 Queue 接口继承的方法完全等效于 Deque 方法,如下表所示:
| Queue 方法 | 等效 Deque 方法 |
|---|---|
| add(e) | addLast(e) |
| offer(e) | offerLast(e) |
| remove() | removeFirst() |
| poll() | pollFirst() |
| element() | getFirst() |
| peek() | peekFirst() |
3、可用作于栈
Deque实现了Queue,自然而然是一个队列。但双端队列也可用作 LIFO(后进先出)堆栈。应优先使用此接口而不是遗留 Stack 类。在将双端队列用作堆栈时,元素被推入双端队列的开头并从双端队列开头弹出。堆栈方法完全等效于 Deque 方法,如下表所示
| 堆栈方法 | 等效 Deque 方法 |
|---|---|
| push(e) | addFirst(e) |
| pop() | removeFirst() |
| peek() | peekFirst() |
补充:Queue 实现通常不允许插入 null 元素,尽管某些实现(如 LinkedList)并不禁止插入 null。即使在允许 null 的实现中,也不应该将 null 插入到 Queue 中,因为 null 也用作 poll 方法的一个特殊返回值,表明队列不包含元素。
4、可用作于列表
LinkedList实现了List接口,自然拥有List的特性。关于List的特性,可参考ArrayList,这篇更多讨论的是除List接口之外的更多特性。
三、方法说明
结合前文所述,我们看下LinkedList对于方法addFirst(e)、addLast(e)、removeFirst()、**peekFirst()**的具体实现(抽取队列和栈的各自特点)。不过在此之前,我们先来看下构造方法。
1、构造方法
两个构造方法如下
public LinkedList() {
}
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
// 遍历Collection,将其添加进LinkedList
addAll(c);
}
2、addFirst(e)
都是链表的常规操作。
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
private void linkFirst(E e) {
// final表示不可更改,这里的final可有可无
final Node<E> f = first;
// 构造方法为 Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next)
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
// 修改次数增1(继承自AbstractList),标记并发
modCount++;
}
假设1:链表为空,即first = null, last = null,f = null
那么方法执行过后,first = newNode, last = newNode
假设2:链表先前存在1->2->3,现插入0
那么方法执行过后,first = 0, first.pre = 0
3、addLast(e)
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
4、removeFirst()
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
// 为空抛出异常
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item;
final Node<E> next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next;
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
5、peekFirst()
public E peekFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
其他方法不再赘述。
四、面试题
LinkedList设计的很巧妙,这里不拍马屁了。下面针对网上的面试题,再次深入理解下队列和栈。
1、俩栈实现队列
先看图

这里的难点在于,是否两个栈是否分工明确。即把一个栈当作输入栈、一个栈当作输出栈时,题目迎刃而解。实现代码如下
public class MyQueue<E> {
private Deque<E> input;
private Deque<E> output;
public MyQueue() {
input = new LinkedList<>();
output = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void offer(E e) {
input.push(e);
}
public E poll() {
if (output.size() != 0) {
return output.pop();
}
while (input.size() != 0) {
E e = input.pop();
output.push(e);
}
return output.pop();
}
public void pollAll() {
System.out.print("队列输出顺序为:");
while (input.size() != 0 || output.size() != 0) {
System.out.print(poll() + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyQueue<Integer> queue = new MyQueue<>();
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
System.out.println(queue.poll());
queue.pollAll();
queue.offer(4);
queue.offer(5);
queue.offer(6);
queue.pollAll();
}
}
输出结果如下
1
队列输出顺序为:2 3
队列输出顺序为:4 5 6
2、俩队列实现栈
先看图
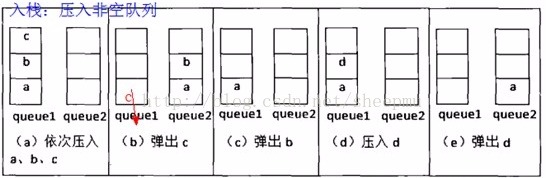
这里的难点在于理解队列最后一个元素,通过落下队列的最后一个元素从而实现栈结构。实现代码如下
public class MyStack<E> {
private Queue<E> queue1;
private Queue<E> queue2;
public MyStack() {
queue1 = new LinkedList<>();
queue2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(E e) {
if (queue2.size() != 0) {
queue2.offer(e);
} else {
queue1.offer(e);
}
}
public E pop() {
if (queue1.size() > 0) {
while (queue1.size() > 1) {
E e = queue1.poll();
queue2.offer(e);
}
return queue1.poll();
}
while (queue2.size() > 1) {
E e = queue2.poll();
queue1.offer(e);
}
return queue2.poll();
}
public void popAll() {
System.out.print("栈输出顺序为:");
while (queue1.size() != 0 || queue2.size() != 0) {
System.out.print(pop() + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyStack<Integer> stack = new MyStack<>();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
stack.popAll();
stack.push(4);
stack.push(5);
stack.push(6);
stack.popAll();
}
}
输出结果如下
栈输出顺序为:4 3 2 1
栈输出顺序为:6 5 4 ;
总访问次数: 372次, 一般般帅 创建于 2017-09-20, 最后更新于 2020-06-25
 欢迎关注微信公众号,第一时间掌握最新动态!
欢迎关注微信公众号,第一时间掌握最新动态!